Training of the Club's Board and Executive Committee of the Union: Session 3 - Project Planning Skills
Following two training sessions on relationship-building skills and work organization and management skills, the Faculty of International Relations continued to organize a training course for members of the Club's Board and Executive Committee of the Union, session 3 - Project Planning Skills. The training session aims to develop project objectives, action plans, and control during project implementation by the Management Boards of the Clubs under the Faculty and the Executive Committee of the Union.

The training will take place at 16:00, Saturday, September 18, 2021, via online format via the Zoom platform. Participants in the training included the Dean of the Faculty of International Relations, the Club's Board, and the Executive Committee of the Union; Students who are club members and collaborators of the Union have the desire to apply to the Executive Committee of the Club and the Executive Committee of the Union.
The guest is Hoang Ba Minh, the first output valedictorian of the Marketing major at the University of Economics and Finance, Ho Chi Minh City (UEF), Partnership Lead, GIVE IT BACK project, Head of Education, NFX1 Group, Ufresh at Ecommerce Channel, Unilever.
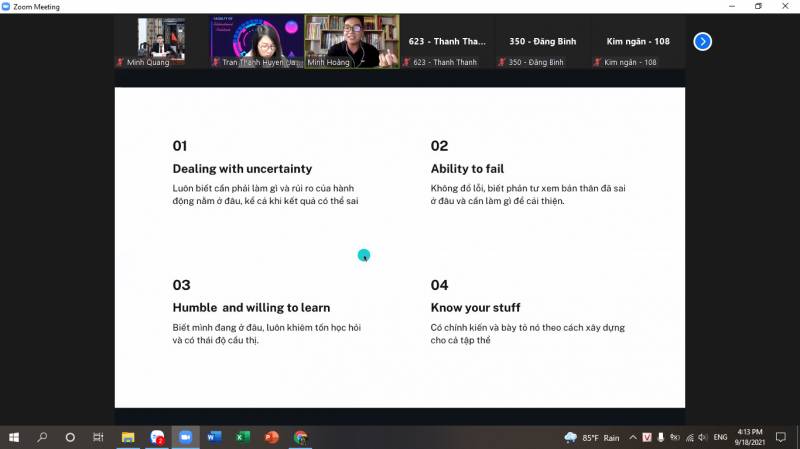
At the beginning of the training session, Mr. Minh shared four factors in the Founder Test of the Give It Back organization: solving unexpected problems, the possibility of failure, humility, and willingness to learn and recognize your problems. This test will help students always know what they need to do, determine where the risk of action lies, identify where they are wrong and what to do to correct the consequences.
To give the students an initial understanding of planning, the speaker emphasized the importance of taking time to plan:
Planning helps us to know the purpose of action, why and how to do it.
Therefore, the team will focus on the essential things in implementing the plan to arrange a suitable time.
In addition, to plan other aspects in the process of activities as well as in life.
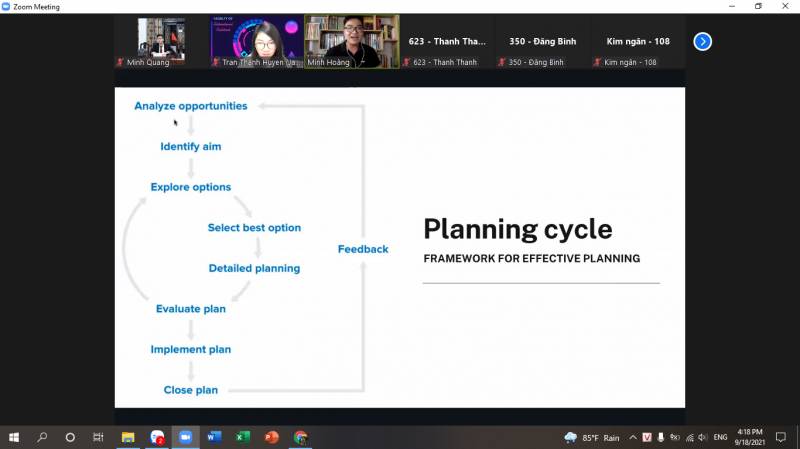
Next, Mr. Minh introduced and analyzed to the students the planning cycle. That model includes the following steps: (1) opportunity analysis; (2) goal identification; (3) forming options; (4) choose the best option; (5) detailed planning; (6) evaluation of the plan; (7) contingency planning; (8) complete the plan. In particular, this entire planning process is constantly evaluated and feedbacked to identify limitations or problems with the plan.
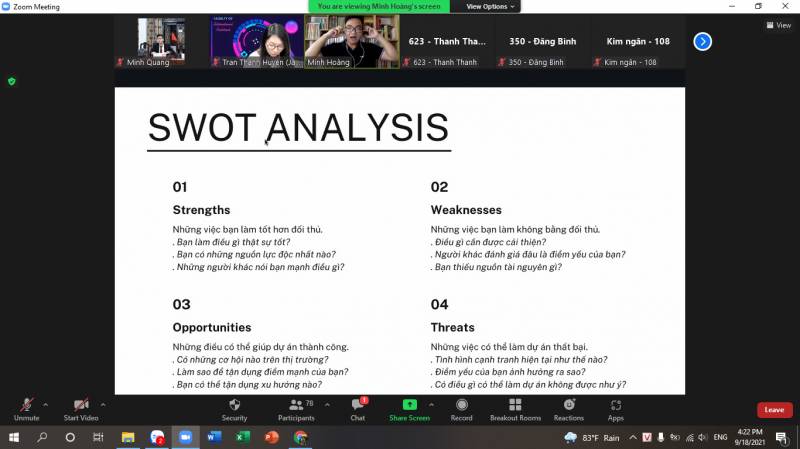
Providing more tools for students in planning, Mr. Hoang Ba Minh focused on two models: SWOT and risk analysis. The SWOT model is familiar to students; this model includes 04 factors: strengths, limitations, opportunities, and risks. In terms of forces, you need to determine what things you do better than the opponent; those must be different, unique characteristics. In addition, Dr. Tran Thanh Huyen also emphasized that strength must combine many forces that others do not have. Regarding the limitations, the team needs to recognize what the individual/team needs to improve and find those weaknesses. In addition, students need to research opportunities to know what opportunities or trends are available in the market. Finally, regarding risk, you need to answer questions such as: how is the competition? How will the weakness affect the plan?
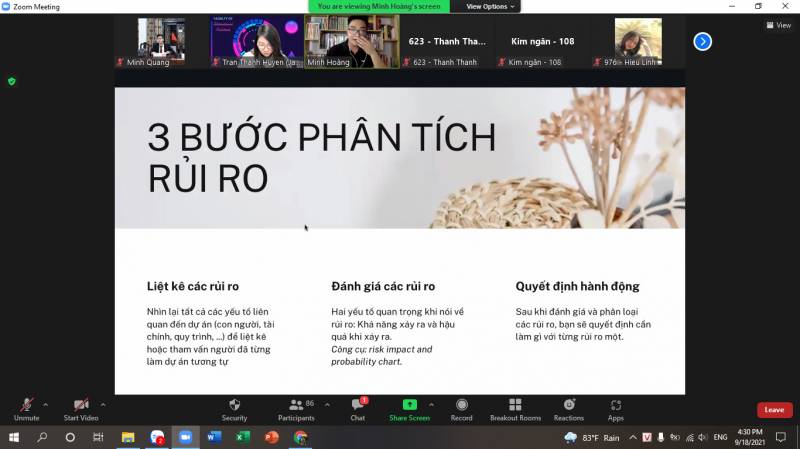
The second model that the speaker introduced is risk analysis - the process of controlling for disadvantages. This model includes three steps: (1) enumerate risks; (2) risk assessment; (3) decide to act. Listing risks is the step of looking back at all the factors related to the project (people, finances, processes) to consult with people who have done similar projects. The risk assessment step has two important issues: the likelihood of the risk occurring and the consequences when the risk has occurred. Finally, after assessing and classifying risks, we will decide what to do about each risk.
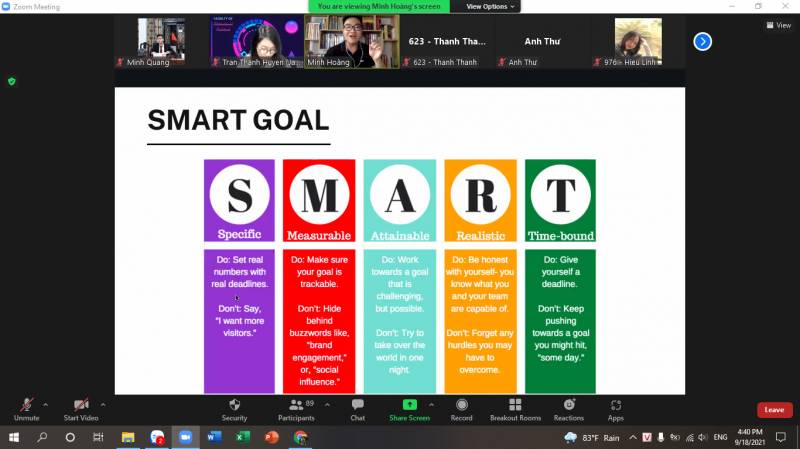
Regarding tools for planning, Mr. Minh suggested SMART GOAL diagrams and brainstorming methods. SMART goals are essentially established principles to shape and accomplish future goals. The content of SMART goals includes:
- Specific: easy to understand: An intelligent goal must first be planned in a specific and transparent way—the more detailed and precise the purpose, the clearer the determination and effort to implement.
- Measurable: This principle implies that goals must be tied to numbers. The SMART focus ensures that your plans have weight, namely weight, measure, measure, count.
- Attainable: we have to think about the possibility of implementing the plan.
- Realistic: the goal you design for yourself must stick to reality and the resources you have available.
- Time-bound: This rule gives you a milestone that determines when you complete the plan. In the process, you know where you are going and make timely adjustments when necessary.
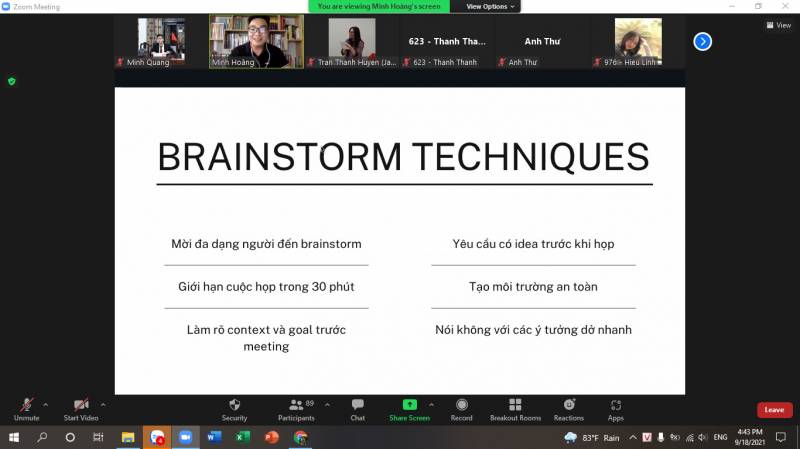
Referring to brainstorming skills, Mr. Minh noted the following points: there should be a diversity of subjects participating in brainstorming; prepare ideas before the meeting; meeting time limit is 30 minutes; create a safe meeting environment; clarify the context and goals before the meeting; get rid of new ideas quickly.
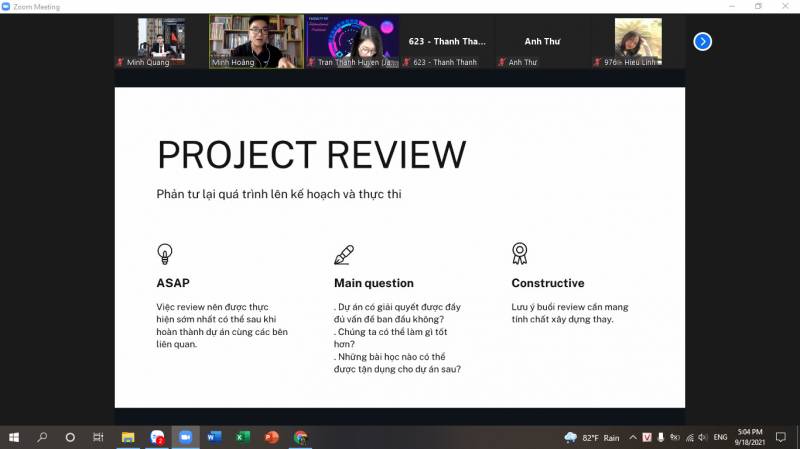
Finally, in his sharing, Mr. Minh emphasized looking back at the entire planning process. Here, Mr. Minh advises students to conduct a learning meeting as soon as possible with all stakeholders after the event has ended. Focus on answering questions such as: Has the project solved the problem? What can we do better? What lessons can be used for future projects?. In particular, the spirit of the meeting needs to be constructive, contributing ideas so that the team can work more effectively in the following tasks.
Through the sharing of Mr. Hoang Ba Minh and Dr. Tran Thanh Huyen, the Club's Board and Executive Committee of the Union members understood the project development objectives, how to implement the action plan, and manage the risks of the upcoming project implementation.










